Experimental study on the factors affecting cement bond strength at the first interface of oil-gas well
1
CNPC Engineering Technology R&D Company Limited, Beijing 102206, China
2
School of New Energy and Materials, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu 610500, China
Submission date: 2024-06-17
Final revision date: 2024-12-23
Acceptance date: 2026-01-22
Publication date: 2026-02-09
Cement Wapno Beton 30(3) 232-243 (2025)
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
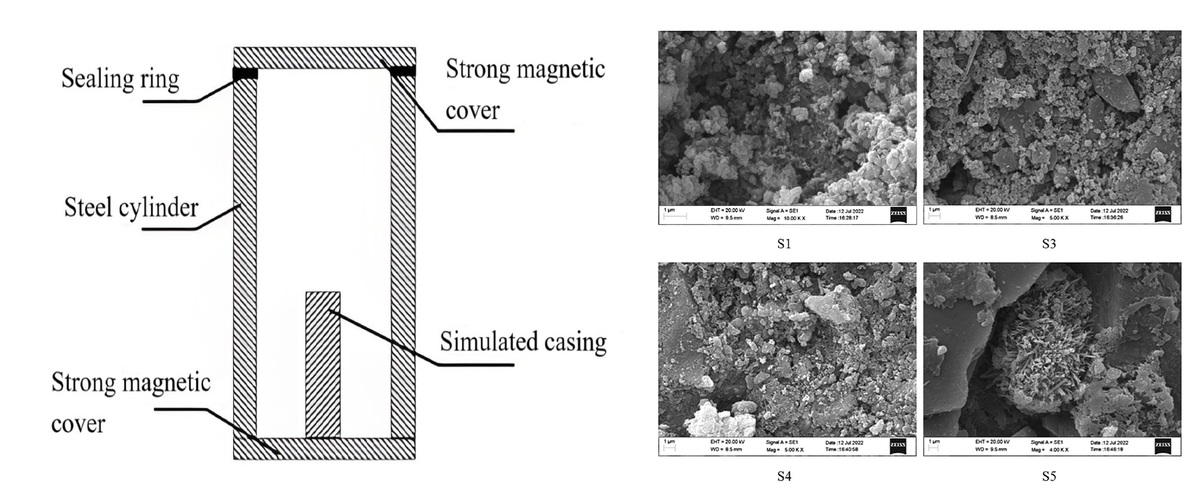
The first cementing interface refers to the interface between the cement sheath and the casing after the cement injection is completed. The bonding strength of the first cementing interface is mainly generated by the interaction between the outer surface of the casing and the cement sheath. This article explores the influence of cement strength on the first interface of cementing by changing the water-cement ratio of the cement slurry system, adding ultra-fine materials, and changing the type of fluid loss control additive. Cement slurry types were selected in the form of progressive experiments, including pure cement slurry systems [L1, L2] under different water-cement ratios, cement slurry systems [L3] based on pure cement systems mixed with nano-silica, and the addition of different types of fluid loss control additives [S2-S4] and cement slurry system [S5] with fluid loss control additives and latex added together. Through the self-developed cementing strength evaluation mold and the microscopic characterization of the cementing interface, the influencing factors of the cementing strength of the first interface of the cement sheath were explored. The results show that increasing the water-cement ratio or adding nano-silica can promote the formation of hydrated calcium silicate [C-S-H], with lower early strength but higher later strength; adding a fluid loss control additive can increase the content of calcium hydroxide crystals [CH], the close packing of CH and without hydration reacting cement particles can provide the first interface cementing strength; the reaction of the latex particles themselves to form a three-dimensional network structure can improve the cementing strength, but it is not suitable for high-temperature environments. This research is of great significance to the summary of cementing-interface cementing laws and the cementing construction process.
REFERENCES (25)
1.
W. Zhai, C. Wang, X. Yao et al. Characteristics of polycarboxylate-based dispersant suitable for medium and low temperature oil well cementing. Constr. Build. Mater. 290, 123239 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb....
2.
N. Agofack, S. Ghabezloo, J. Sulem et al. Experimental investigation of the early-age mechanical behaviour of oil-well cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 117, 91–102 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemc....
3.
L. Ming, D. Shuang, Y. Yongjin et al. Mechanical properties and microstructure of oil well cement stone enhanced with tetra-needle-like ZnO whiskers. Constr. Build. Mater. 135, (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb....
4.
B. Zhang, Z. Peng, C. Zou et al. Study on surface modification of CaSO₄ whisker and mechanism of enhancing mechanical properties of oil-well cement. Colloids Surf. A 618, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cols....
5.
Y. Bu, L. Tian, B. Guo et al. Experiment and simulation on the integrity of cement ring interface in deep water shallow formation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 190, 107127 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petr....
6.
Z. Yijin, L. Peiqing, T. Qian et al. Experimental study and analysis on the microstructure of hydration products on the well cementation second interface and interface strengthening strategies. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 207, 109095 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petr....
7.
S. Stryczek, A. Gonet, M. Kremieniewski, Special cement slurries for strengthening salt rock mass. Energies 15, 6087 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/en1516....
8.
M. Kremieniewski, Influence of Hblock fine-grained material on selected parameters of cement slurry. Energies 8, 2768 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/en1508....
9.
H. Zhang, Experimental Study on Prediction of Cement Sheath Failure. China University of Petroleum, Beijing (2020).
10.
G. Yang, K. Liu, X. Zeng, R. Liu, J. Ai, L. Hao, Experimental analysis and discussion on cement sheath failure caused by the varied casing internal pressure in shale gas wells. Sci. Technol. Eng. 21, 5311–5317 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petr....
11.
M. Fan, Study on the Casing Deformation and the Cement Sheath Sealing Failure Mechanism during the Shale Well Volume Fracturing Process. China University of Petroleum, Beijing (2018).
12.
P. Huang, Y. Li, D. Li, H. Fan, D. Liu, Experimental study on radial cementation strength of the first cementing interface in HTHP wells. China Pet. Mach. 49, 39–44 (2021). https://doi.org/10.16082/j.cnk....
13.
X. Lin. Analysis of the influence of cementing cement slurry performance on cementing quality. Sci. Technol. Innov. 16, 83 (2022).
14.
Y. Yan, Z. Guan, J. Jiang, W. Yang, Experimental study on crack characteristics of cementing cement under the action of shaped charge jet. J. Xi’an Shiyou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 35, 55–61 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn....
15.
X. Wu, D. Li, Q. Bian et al. Preliminary study of a composite process in concrete manufacture. Cem. Concr. Res. 17, 709–714 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8....
16.
K.O. Kjellsen, B. Lagerblad, Microstructure of tricalcium silicate and Portland cement systems at middle periods of hydration—development of Hadley grains. Cem. Concr. Res. 37, 13–20 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemc....
17.
M. Zu, Accurate Interpretation and Evaluation of Complex Structure on Puzaoying Area of Langgu Sag. Yangtze University (2013).
18.
C. Li, Study on the Technology of Improving the Interfacial Sealing Quality of High Permeability and Low Pressure Layer in Changyuan Oilfield. Northeast Petroleum University, Heilongjiang (2016).
19.
L. Jiao, K. Yao, C. Li, N. Mou, F. Wang, Y. Zheng, The influence of isolation fluid materials for cementing on the quality of interface bonding. Drill. Prod. Technol. 42, 104–107 (2019).
20.
Z. Jian, Y. Guang, K.V.B. Klaas, Characterization of pore structure in cement-based materials using pressurization–depressurization cycling mercury intrusion porosimetry (PDC-MIP). Cem. Concr. Res. 40, (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemc....
21.
L. Zhang, Q. Mao, W. Wu et al. Research on improving the impermeability of cement-based materials through interface modification of water absorbing microcapsules. Silic. Notif. 41, 2663–2671 (2022). https://doi.org/10.16552/j.cnk....
22.
M. Kremieniewski, S. Stryczek, Use of calcium aluminate cements as binders in sealing slurries for drilling technologies. Cem. Wapno Beton 22(3) 215-226, (2019).
23.
B. Wang, R. Wang, The hydration law of cementing cement slurry. J. China Univ. Pet. 34, 66 (2010).
24.
J. Bao, Y. Li, B. Xie, Research progress on pore structure of cement concrete. (2010).
25.
A. Pikłowska, J. Ziaja, M. Kremieniewski. Influence of the addition of silica nanoparticles on the compressive strength of cement slurries under elevated temperature condition. Energies 14, 5493 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/en1417....
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.